As a homeowner, you take pride in maintaining a safe haven for yourself and your family. However, without the proper surveillance, a number of factors can threaten your health and safety within the walls of your home. For instance, radon concentration is a notorious threat to homes across the country, with concentration levels varying based on a number of environmental and structural factors. To learn more about radon, your home’s radon concentration and how to limit your radon exposure, check out the following helpful information.
What is Radon?
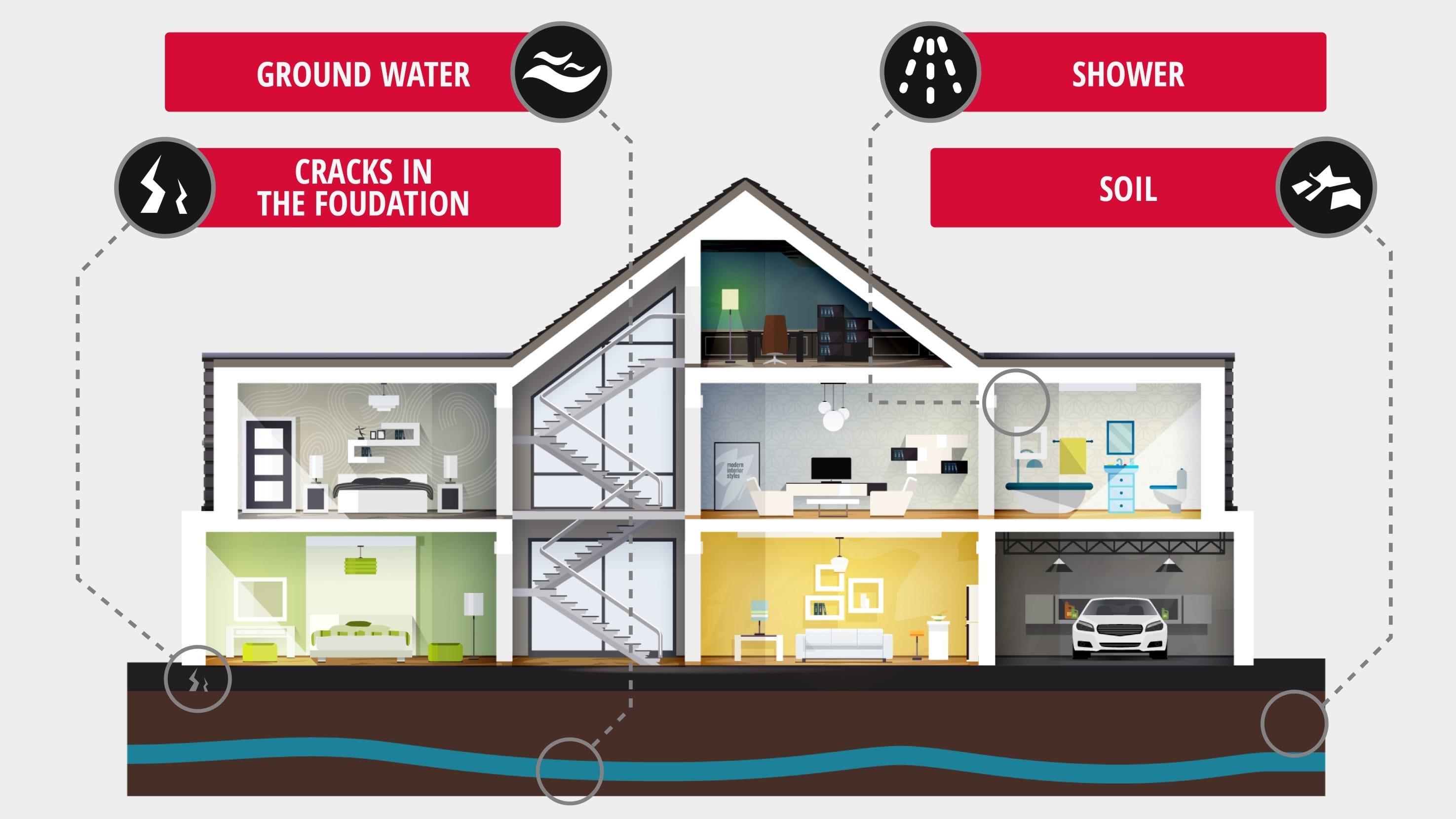
In order to limit the threat of radon in your home, it’s important to understand exactly what it is and where it comes from. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, radon is a naturally-occurring radioactive gas that is both colorless and odorless. In nature, radon disperses quickly into the atmosphere and causes minimal health issues. However, radon can leak into homes through cracks in the foundation. When trapped inside, it can lead to a host of medical issues, particularly when the individuals have been exposed to the radon for many years.
As a person breathes in radon, their lungs are exposed to small amounts of radiation that can significantly damage their cells and even lead to various types of cancer. Though it may be surprising, radon exposure is currently the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States, with smoking as the leading cause. While radon poses a serious threat to homeowners and their families, the good news is that it can be identified and controlled with regular radon testing.
Do All Homes Have A Radon Concentration?
As mentioned above, radon generally does not create any problems in its gaseous form outdoors, since it dissipates rapidly into the atmosphere. However, when contained in buildings such as homes, schools or hospitals, for example, it can become highly dangerous for those inside the building. The effects of trapped radon only worsen over time, which is why it is so important to control its concentration level.
That being said, how can you determine whether or not your home has a higher than recommended radon concentration? More likely than not, there is at least a small level of radon concentration in your home, even if you have a mitigation system in place. According to the Environmental Protection Agency, 1 out of every 15 homes is estimated to contain elevated levels of radon, while some geographic areas have even higher odds. The average radon concentration in the United State is between 1-3 picocuries per liter (cPi/L), but some homes contain radon concentrations as high as 80 pCi/L or more. If your radon test shows a concentration of 4 pCi/L or more, it’s time to take action. A radon mitigation system can effectively reduce your home’s radon concentration by up to 99%.
In order to reduce radon accumulation in homes, more and more builders are adopting radon-resistant construction techniques to protect residents’ health and safety. However, even if your home has been built using radon-resistant techniques, it’s still essential to test the home for radon upon moving in.
What Determines A Home’s Radon Concentration?
While it is not unusual for a home to contain a limited amount of radon (2.7 cPi/L or lower is ideal), radon concentration is largely determined by environmental and structural conditions. Radon itself is a result of the natural decay of uranium, an element which is present in nearly every type of soil. As the uranium decays, it releases radon into the surrounding soil, which rises up and seeps through any cracks or holes in homes’ foundations. Over time, the radon accumulates and becomes increasingly dangerous for residents, who unknowingly breathe in the radioactive gas day after day.
The second most common source of radon concentration – after soil – is water supply. Although it is less likely that radon will enter your home through the water supply than through soil, it is still a possibility that should be taken seriously. For example, well water can contain radon, which can be a health risk for residents when they breathe in radon that’s released during showers. Drinking water containing radon can also lead to cases of stomach cancer, but studies show that inhaling radon that can cause lung cancer is the bigger risk. It’s always a good idea to test your water for radon, especially if you source your water from a private well.
Lastly, radon can also enter a home through the decay of construction materials such as brick, marble and granite, but this is a much less common point of entry than through soil or water.
Concerned About Your Home’s Radon Levels? Take Action Now
Because radon has no odor or color to indicate its presence in your home, it is crucial to regularly test your home for radon concentration. This is the only way to ensure that you and your family are not inhaling or consuming dangerous amounts of radon, either through the air or water supply. As previously mentioned, when radon accumulates in a home, residents unknowingly inhale the radioactive gas, which then damages the cells in their lungs. Though less common, when consumed in water, it can lead to serious health issues such as stomach cancer.
Hiring M.A.R.S. Environmental to test your home’s radon concentration is the first step to maintaining a safe and healthy home. Not only we will determine your home’s current radon concentration, we will also help you decide what mitigation measures should be taken to reduce your home’s future radon accumulation. If you haven’t tested your home for radon recently, or you’re about to move into a new home, contact M.A.R.S. Environmental. Take a look at the following ways to reduce the risk of radon exposure in your home.
Strategies to Reduce Your Risk of Radon Exposure
If you are concerned about your home’s radon concentration, time is of the essence. Because radon can be such a danger to residents’ health, an intervention is necessary as soon as a problem is detected. Start by contacting M.A.R.S. Environmental and asking for a professional to come to your home and test its radon concentration. If, for some reason, M.A.R.S. Environmental cannot come to your home immediately, there are a few strategies that you can implement to temporarily reduce the risk of radon exposure in your home.
The first way to reduce your and your family’s risk of radon exposure is to eliminate the radon’s points of entry into your home. Because radon is a result of the decay of uranium, it is found in a number of different types of soil. Once emitted into the soil, the radon rises up toward your home’s foundation. If there are any holes or cracks in the foundation, the radon will inevitably seep in. However, it can also enter your home through cracks under doors, windows or other points of entry. To limit radon accumulation, try sealing the cracks around doors and windows in your home using caulk or foam insulation. Opening doors and windows a few hours each day can be helpful too. This should only be used as a temporary measure before a radon mitigation expert has the chance to intervene. However, it’s imperative that all doors and windows are closed for at least several days before testing to get an accurate, indoor radon level result.
How Often Should You Test Your Home For Radon?
Although it may be easy to overlook or postpone, radon testing should be a top priority for all homeowners. After all, the more vigilant you are about reducing the radioactive gas in your home, the healthier you and your family will be. That being said, how often should you test your home’s radon concentration? If you already have a radon mitigation system installed in your home, you should continue to have your home tested every two years at minimum.
Additionally, if your home was constructed in or after 1978, you should perform radon tests every two years. This rule has to do with home construction techniques that were implemented in 1978 which tend to lead to higher radon levels. Because older homes were not built with these techniques, they tend to have lower radon levels. Even so, it’s crucial to test your home’s radon concentration on a regular basis, so that you and your family can stay as safe as possible.
Protect Yourself and Your Family From Radon Concentration
Colorless and odorless, radon is a radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes and cause serious health problems for residents. Although most homes contain some level of radon, it is crucial to perform regular radon testing in order to keep its concentration below 4 cPi/L. Above this level, radon concentration can lead to significant health issues for a home’s inhabitants, including lung or stomach cancer. To reduce this risk, M.A.R.S. Environmental can test your home’s radon concentration and recommend a mitigation system if necessary. M.A.R.S. Environmental will intervene in a timely manner to evacuate the radon that’s accumulated in your home, effectively making your home a safer, healthier place. Contact M.A.R.S. Environmental today.
Sources:
https://www.epa.gov/radiation/what-radon-gas-it-dangerous
https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2016-02/documents/2012_a_citizens_guide_to_radon.pdf